Why Greeks and Turks are NOT similar to each other
Aims of the following article:
1)to highlight the cultural, linguistic, racial and mental differences between Greece and Turkey, which, in case of Greece, represent the 90% of Greek identity, especially in terms of Greeks proper
2) along with the historical reasons that lead to this conclusion, in order to respond to the question “what are some similarities between Greeks and Turks”.
1)to highlight the cultural, linguistic, racial and mental differences between Greece and Turkey, which, in case of Greece, represent the 90% of Greek identity, especially in terms of Greeks proper
2) along with the historical reasons that lead to this conclusion, in order to respond to the question “what are some similarities between Greeks and Turks”.
Turkish vs
Greek Culture
Considering
at least 4 aspects of culture, Architecture, music/dances, folk costumes and
cuisine, Greek culture is clearly distinguishable from Turkish, with Greek
being clearly shifted towards Latin speaking countries (and sometimes
South-east European countries) and Turkish towards the middle east (Arabic
countries), and sometimes Central Asia (Uralic-Altaic countries)
Mainstream
Greek architecture:
The same goes for folk Music, Greek folk Music:
Turkish folk music:
The same
goes for folk costumes, since some people take them into consideration:
Greek:
For comparison, Sardinian (an equally Mediterranean European nation)
Turkish Folk costumes:
Turkish and
Greek similarities, from these aspects can occur to a low degree only in terms
of Turks and “inner Anatolian Greeks” (such as Cappadokian Greeks), because of Byzantine originated similarities (not central Asian) with Greek groups which used to live in Turkey
until 1923, and today they live mainly in northern Greece. However, when we are
talking about Greeks proper (from mainland, especially the south, and the
islands), the differences are obvious.
Linguistically,
the two languages are completely different, with Greek being an Indoeuropean
language, with a pronunciation commonly accepted as similar to Romance
languages, meanwhile Turkish language and accent are Altaic-central Asian.
Of course
both languages can share words from each other, but at least in terms of Greek
language, along with 300 common Turkish words, it also shares 400 italian, and
a similar number of words from other European languages.
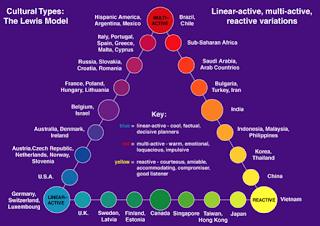
By
mentality, the Lewis model clarifies the differences, with Greece, once again
being associated with Southern European countries:
The last
but not least, Race (genetics and racial types). In terms of racial types, only
pigmentation seems to be similar in both countries. But the facial structure is
completely different in the majority of Greeks and Turks, with Greeks mostly
having Mediterranean and Alpine types (see Coon, 1939), and Turks having mostly
anadolid, and some times even Turanid types.
But even
genetically, in all pca (genetic graphs), Greece is clearly a Southern European
country, meanwhile, Turkey is a middle eastern country with some European as
well as East Asian (mongoloid) influence, both effects being reflected not only
in official studies, but in personal results as well (Gedmatch etc)
The
misconception that Turks and Greeks have many similarities, is related to 2
main factors: The Byzantine originated similarities between Turks and inner Anatolian Greeks (a Greek group which is not included in this article), and the attempt of Turkey’s Europeanization,
which naturally made the particular country to look first at its closest
European neighbor. The common Mediterranean climate would also be a factor
However,
from a historical point of view, there was no reason for Greeks proper and
Turks, to end up similar with each other. For a little less than 400 years
(unlike other Southeastern countries which remained for more than 500 years as
Ottoman, and obviously share similarities with Turkey), most of Greeks were forced to pay taxes to the Ottoman empire, as
part of it.
But then again, apart from the fact that there were non-Ottoman
parts of Greece, either we talk about Venetian ruled Ionian islands, along with
some Aegean islands, or about Autonomous and independent parts of the mainland
(see main etc), even the fully Greek ruled parts of Greeks, did not have more
contacts than just paying taxes to the Ottoman empire. In most of the country
there were not even Turkish communities.
The conclusion:Either Greece and Turkey are not similar, or Turkey is similar to Romance countries too. I would choose the first, as at least for an experienced eye, The difference between Turkish and Mediterranean European culture is huge
The conclusion:Either Greece and Turkey are not similar, or Turkey is similar to Romance countries too. I would choose the first, as at least for an experienced eye, The difference between Turkish and Mediterranean European culture is huge





























Σχόλια
Δημοσίευση σχολίου